IMPROVEMENT OF AGRI-FOOD PRODUCTION AND INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGIES FOR A HEALTHIER, SAFER AND SUSTAINABLE NUTRITION
sPATIALS3 project strategic target has been the creation and the strengthening of a Lombard network within the agri-food supply chain, dedicated to human nutrition and capable of providing technologically advanced solutions in the agri-food sector.
Agri-food products, with nutritional properties and effects on the global population, have been optimized optimized for at-risk subjects with specific pathologies like the metabolic syndrome, with neuro-motor problems or with peculiar nutritional needs.
Further cornerstones of the project are the advanced metabolomics and proteomics platform and the study of the microbiota, for:
- The improvement and selection of primary products, so that they are more responsive to new market demands and have a lower environmental impact;
- guarantee the quality, safety and traceability of the matrices at the origin and after packaging for sustainable consumption;
- obtain food with high nutritional efficiency;
- develop processes based on the concept of biorefinery for the production of fine- and / or bulk-chemicals;
- act on aspects related to nutrition to ensure the well-being of individuals, provide prevention tools and offer support for the management of disabilities of patients in rehabilitation.
PRODUCT CONCEPT AND IMPROVEMENT OF PRIMARY INGREDIENTS

FUNCTIONAL SYNBIOTIC FOR METABOLIC SYNDROME PREVENTION
A clinical study was focused on a dietary supplementation with a combination of the active ingredient Moradyn® and a prebiotic combined with probiotics [Active Synbiotic]. The aim of the study has been to develop a product for different categories of subjects and to understand whether this supplementation can act on the quality of the diet in order to reduce the inflammatory potential and improve absorption, intestinal motility and bowel habit in the selected patients.
The randomized controlled interventional study was coordinated by Centro Nemo which focus was also on patients diagnosed with ALS, by IRCCS-Medea for pediatric patients with neurodevelopmental disorders (ADHD), and by IRCCS-INRCA for elderly patients with chronic diseases (COPD). For each of the pathologies treated, the patients were assigned to two treatment arms: Study Group, GS - to which the active symbiotic preparation was administered; Control Group, GC – administered with a standard symbiotic preparation (prebiotic only and probiotics).
Allocation to the two treatment arms was based on block randomization, with a block size of 4 and an allocation ratio of 1:1. Randomization was done in double-blind, i.e. blinding for patients and investigators (clinicians and outcomes evaluators).
For entering the data collected during the recruitment phase and the subsequent data analysis, together with the data collected from the other participating clinical centres, an electronic medical record (eCRF) was created via the RedCap platform.
At the end of the study, in patients treated with active synbiotic there was a significant increase in the biodiversity of the intestinal microbiota. Furthermore, an increase in the main SCFAs, known for their immunomodulatory action with a positive effect on intestinal health, was highlighted in patients diagnosed with ALS.
IMPROVEMENT AND BREEDING
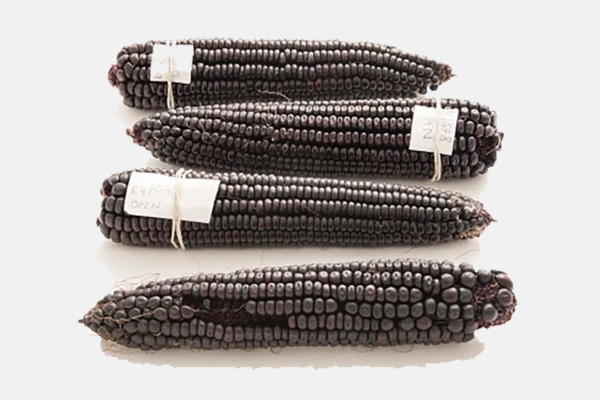
OF LOMBARD PIGMENTED CORN MORADYN®
OF LOMBARD PIGMENTED CORN MORADYN®
ZUCCARO M.*, VITALE A.*, PRINSI B.**, ESPEN L.**, PEDRAZZINI E.*
*) CNR, Institute of Agricultural Biology and Biotechnology, Milano **) University of Milano, DiSAA
Maize seed proteins are mainly constituted by the endosperm-located zein prolamins, which are rich in sulfur amino acids but poor in lysine and tryptophan. However, maize embryo accumulates significant amounts of storage globulins, which are usually the major storage proteins in dicotyledons. Prolamins accumulate in endoplasmic reticulum-derived protein bodies, whereas globulins accumulate in storage vacuoles. Searching for maize varieties with lower content of the allergenic gamma zeins, we have found that Moradyn purple maize has lower content of 27kD gamma-zein and apparently very low content of 50 kD gamma-zein. In a protein body subcellular fraction from Moradyn seeds, we found unusually high amounts of globulin-1S, which is known as a maize embryo vacuolar storage protein and contains almost 4% lysine. Rebalancing of protein content is known to increase embryo storage proteins in maize lines with lower amounts of zeins, but the co-purification of globulin-1S with protein bodies calls for further investigation on the subcellular destiny of this protein in Moradyn seeds.
LXV SIGA Annual Congress From genes to fork - On Mendel's footsteps, Piacenza, Italy, 6-9 September 2022
FLANAT, in accordance the objectives of the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development, will increase the cultivation of new botanical species and their transformation in the Lombard area with the intention of reconverting the traditional agri-food chain by supporting agriculture and the territory by enhancing local agri-food companies. Pursuing this objective, the cultivation of Camelina sativa and pigmented corn was started, selected matrices for the sPATIALS3 Project, whose products and co-products have been used for the development of new foods and functional ingredients with a high nutritional value.
The development strategy for these ingredients focuses sustainability particularly on the agronomic practices adopted in order to reduce the use of pesticides and herbicides, and on the use of green extraction techniques with low environmental impact. The exploitation of co-products obtained from those matrices, through the use of modern transformation systems, will considerably reduce the costs of agricultural processing, opening up new developments both for the territory and for the agri-food industry.
2020-2022












