PASTEL: PIGMENTED MAIZE COBS CO-PRODUCT AS AN ENVIRONMENTAL FRIENDLY SOLUTION TO DYE NATURAL FIBERS
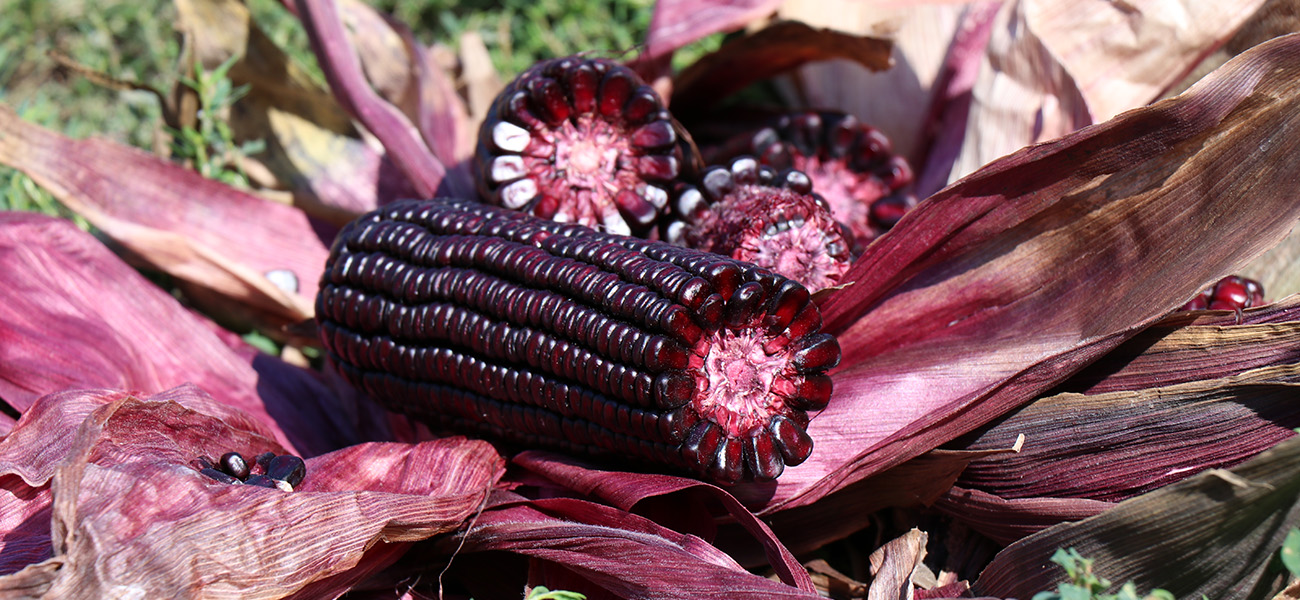
PASTEL project realized new natural dyeing process of natural fibers (mainly wool, silk, cotton and hemp) based on the use of anthocyanins (dyes) and tannins (mordanting) extracted from pigmented maize cobs. Anthocyanins are mainly extracted from red grape skin and other red berries, but since the cultivation of pigmented corn is growing in Lombardy, because of beneficial properties of contained anthocyanins, cobs co-products could become a cheaper source of natural dye.
The development of a low-cost extraction technology starting from cobs co-products represent a correct approach giving new income to SMEs involved in dyeing process and corn cultivation, by integrating this process with the production of functional food rich in anthocyanin or food supplements from corn kernel.
WASTEWATER FROM TEXTILE INDUSTRY IS CLASSIFIED AS THE MOST POLLUTED STREAM
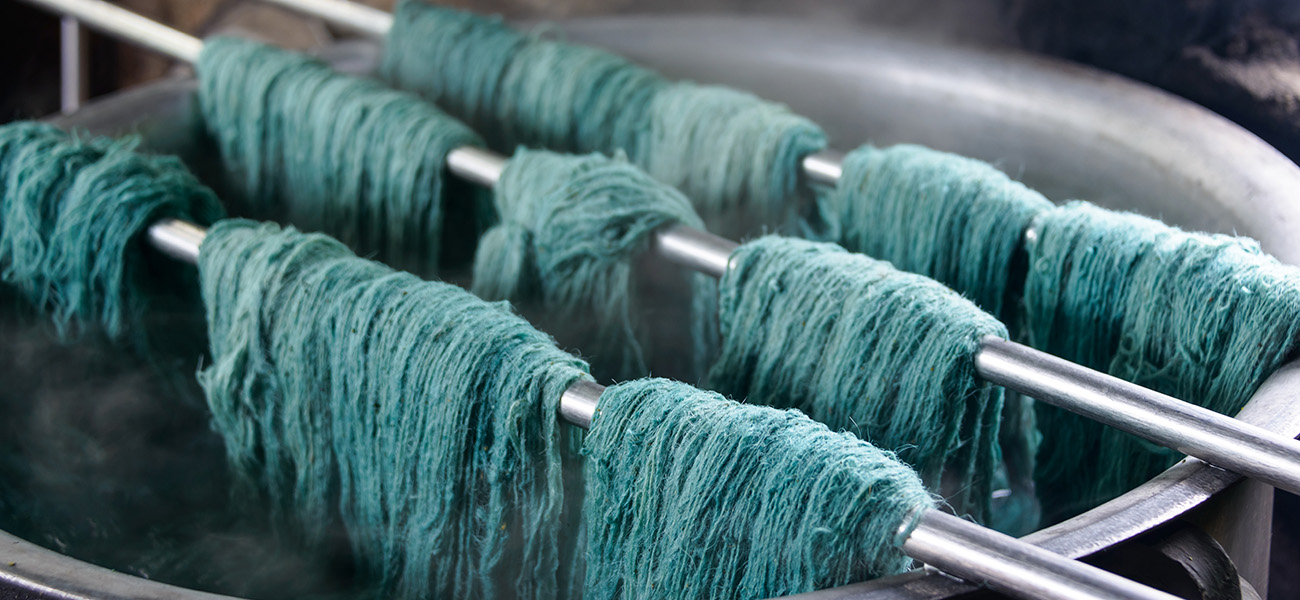

Textile industries, crossways the globe, produce and use approximately 1.3 million tons of dyes, pigments, and dye precursors that cost around $23 billion. Textile production is mainly based on synthetic dyeing materials. Thus, textile industries generate toxic and hazardous chemical wastes which cause a threat to human health and environment (Yu and Bal, 2001).
Textile industry consumes a significant amount of water in its manufacturing processes, mainly during dyeing and finishing dyeing operations. Wastewater from textile plants is classified as the most polluted streams among different industrial sectors, because of both large volume generated and effluent composition. In addition, the increased demand for textile products and the related increase in their production, as well as the use of synthetic dyes, contributed to make dye wastewater one of the main responsible of the severe pollution problems in current times.
For these reason, the use of natural dyes is attracting more and more interests of dyeing industries.
MORADYN CO-PRODUCT AS SOURCE OF NATURAL DYE PIGMENT

Exposure to pollutants threatens the health and well-being of many people living along the coast. In addition to cancer, neurodevelopmental disorders and endocrine dysfunction, heavy metals, constituents of air pollution, organic solvents and food contaminants have been associated to childhood problems with hyperactivity, attention, and impulse control, and to an increased risk of psychiatric diseases, such as schizophrenia and depression, often combined with neurological conditions including highly prevalent pain sensitization. Notably, an increased incidence of psychiatric illnesses is relevant to Mediterranean Countries. The Eastern Mediterranean Region (EMR) is witnessing an increase in mental illnesses, with a prevalence ranging from 15.6% to 35.5%, and more than 100 million sufferers. Depression and anxiety disorders are the most frequent mental disorders in the EMR, with rates in women much higher than in men. Psychiatric disorders also have a large prevalence in the South-Western Mediterranean, where heavy metals and pesticides accumulate in marine animal tissues. Substance-use disorders are very common in all Mediterranean areas, and a strong link between exposure to pollutants and drug addiction has been reported. Importantly, behavioural traits like hyperactivity, compulsion and impulsivity that are common behavioural traits in drug addiction but also in many other psychiatric diseases (e.g. ADHD, eating disorders, OCD, bipolar disorder) are also frequent in Mediterranean countries, and have been associated with exposure to environmental pollutants.
2018-2021











